Below is the media release from AEMO after it suspended the National Electricity market at 14:05 today.
AEMO today announced that it has suspended the spot market in all regions of the National Electricity Market (NEM) from 14:05 AEST, under the National Electricity Rules (NER).
AEMO has taken this step because it has become impossible to continue operating the spot market while ensuring a secure and reliable supply of electricity for consumers in accordance with the NER.
The market operator will apply a pre-determined suspension pricing schedule for each NEM region. A compensation regime applies for eligible generators who bid into the market during suspension price periods.
In making the announcement AEMO CEO, Daniel Westerman, said the market operator was forced to direct five gigawatts of generation through direct interventions yesterday, and it was no longer possible to reliably operate the spot market or the power system this way.
“In the current situation suspending the market is the best way to ensure a reliable supply of electricity for Australian homes and businesses,” he said.
“The situation in recent days has posed challenges to the entire energy industry, and suspending the market would simplify operations during the significant outages across the energy supply chain.”
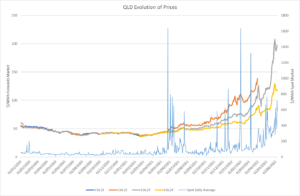
Edge wish to reiterate, this is not a physical supply issue. AEMO directed 5GWhs of physical generation into the market. If generators can operate when under direction, they do not have a physical reason to not generate (such as maintenance, overhaul etc), so the reduced availability we are seeing has to be a commercial trading decision to either price volume into higher price bands or to remove availability in the maximum availability bands of their bids. The availability is there, the generators are just not offering it via the spot market.
The market suspension is temporary, and will be reviewed daily for each NEM region. When conditions change, and AEMO is able to resume operating the market under normal rules, it will do so as soon as practical.
Mr Westerman said price caps coupled with significant unplanned outages and supply chain challenges for coal and gas, were leading to generators removing capacity from the market.
He said this was understandable, but with the high number of units that were out of service and the early onset of winter, the reliance on directions has made it impossible to continue normal operation.
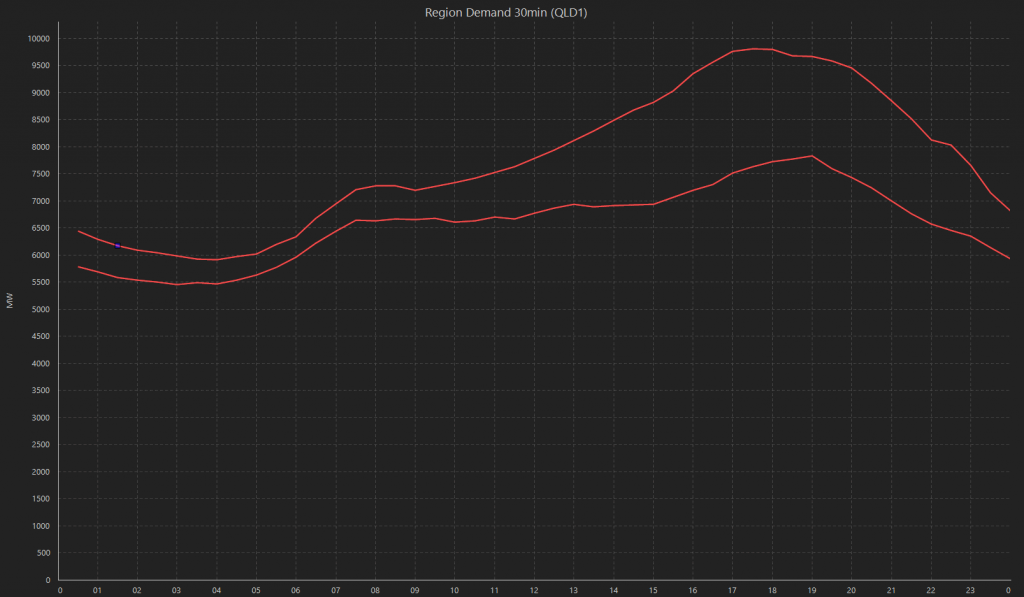
The current energy challenge in eastern Australia is the result of several factors – across the interconnected gas and electricity markets. In recent weeks in the electricity market, we have seen:
- A large number of generation units out of action for planned maintenance – a typical situation in the shoulder seasons.
- Planned transmission outages.
- Periods of low wind and solar output.
- Around 3000 MW of coal fired generation out of action through unplanned events.
- An early onset of winter – increasing demand for both electricity and gas.
“We are confident today’s actions will deliver the best outcomes for Australian consumers, and as we return to normal conditions, the market based system will once again deliver value to homes and businesses,” he said.
What does it mean for generators and end users.
- Bidding and dispatch will continue as usual under the market rules.
- Dispatch instructions will be issued electronically via the automatic generation control system as usual
- If required AEMO may issue dispatch instructions in any other form that is practical in the circumstances.
- Spot prices and FCAS prices in a suspended region continue to be set in accordance with NEM rules or under the Market Suspension Pricing Schedule.
The Market Suspension Pricing Schedule is published weekly by AEMO and contains prices 14 days ahead.
The market will continue to operate under the Market Suspension Pricing Schedule until the Market operator determines the market is able to return to normal conditions and the suspension is revoked.
Article by Alex Driscoll, Senior Manager – Markets, Trading, and Advisory