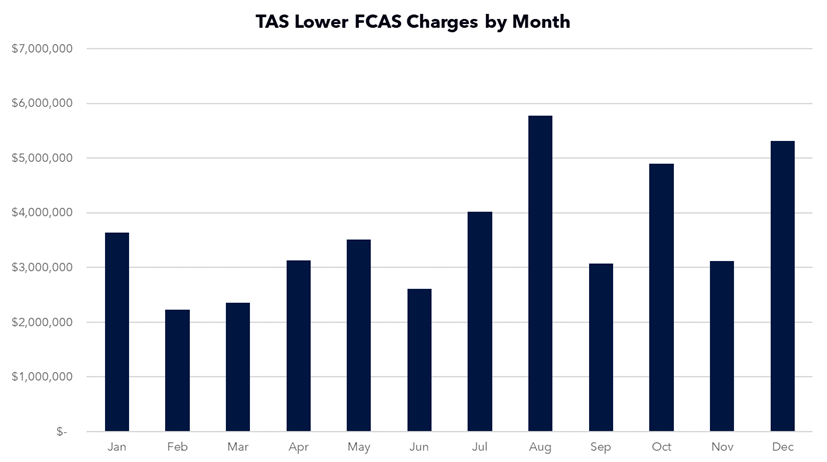
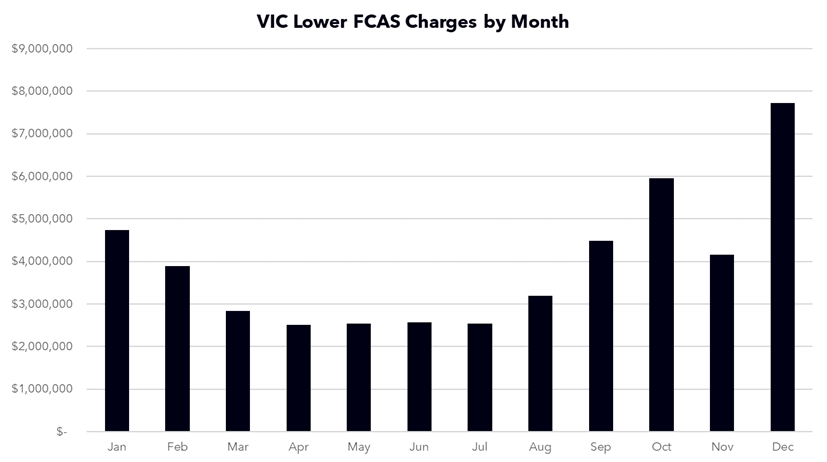
The December 2024 Gas inquiry report by the ACCC was released on Friday, with its focus on the operation of the east coast gas market.
Natural gas is vital to Australia’s transition to lower emissions, supporting energy security, reliability, and affordability as renewables dominate electricity generation. It remains essential for all users including residential, commercial, and industrial users, particularly for manufacturing and chemical processes where alternatives are not viable such as electricity.
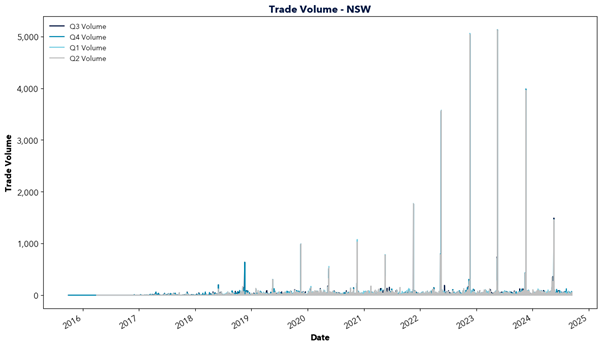
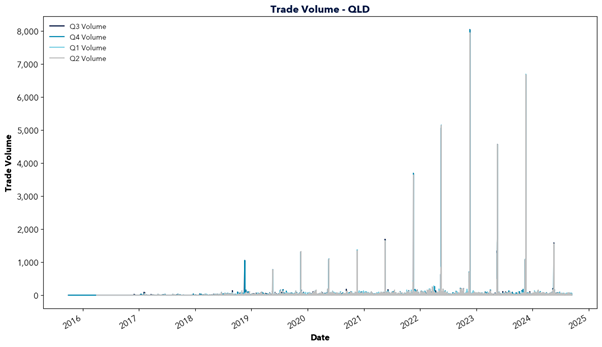
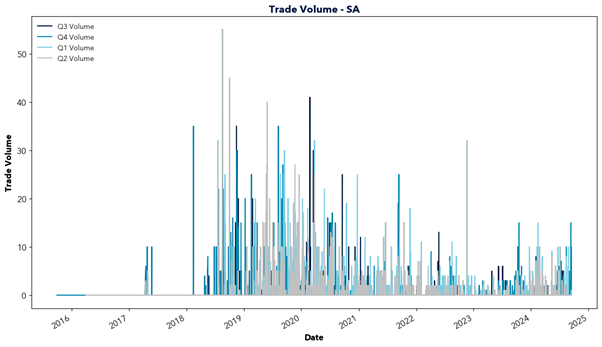
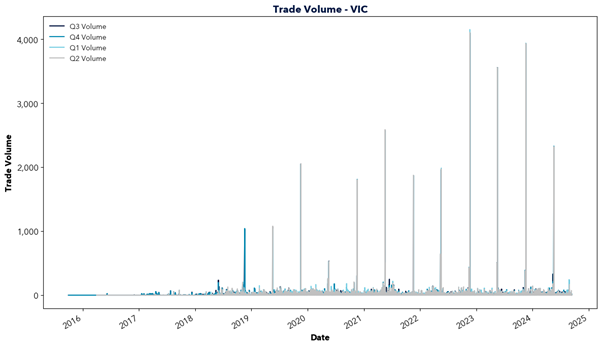
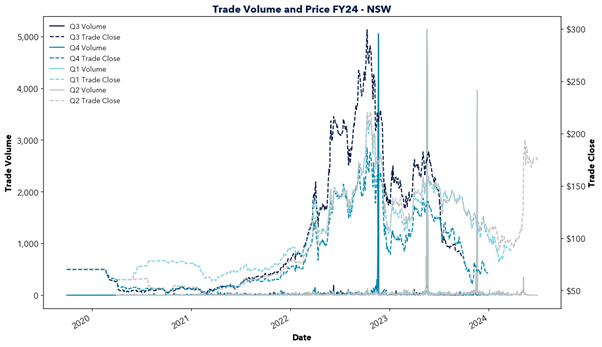
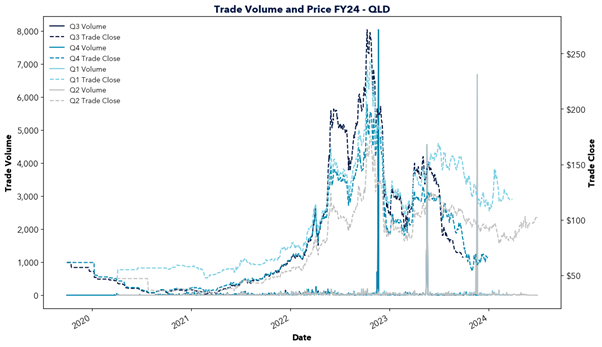
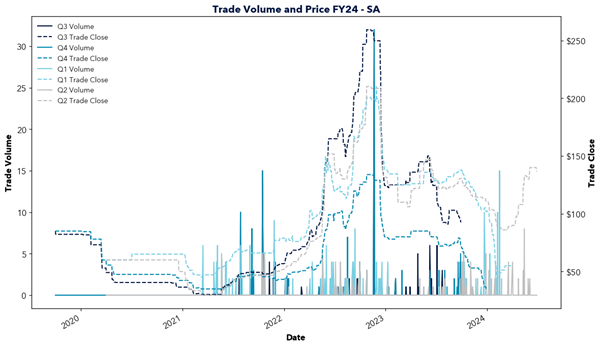
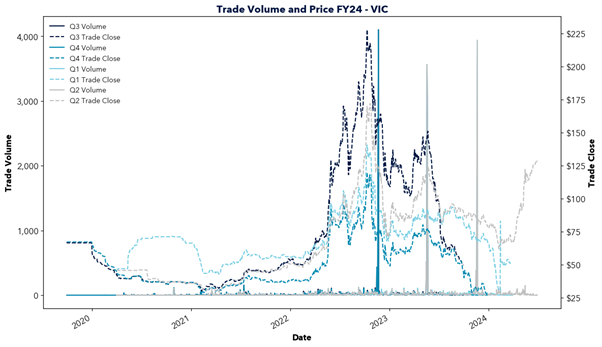
However, east coast gas supply is declining as traditional sources like the Gippsland Basin begin to deplete and new investment lags behind. In the short term, southern states are forecasted to rely upon gas transported from Queensland, facing constraints in pipeline capacity and potential dependence on imported LNG. This will increasingly tie domestic gas prices to international markets and transportation costs, driving up prices locally.
The 2022 energy crisis underscored the risks of inadequate gas supply and the market’s susceptibility to global volatility. To ensure reliability and a smooth transition to lower emissions, the east coast gas market must remain well-supplied as demand for gas is expected to remain high for at least two decades. While residential and commercial demand may decline with electrification, industrial demand will persist due to the lack of alternatives.
AEMO has forecasted that gas-powered generation will grow, requiring additional infrastructure to fill the gap created by intermittent generation from sources like solar and wind until sufficient storage is developed. The ACCC also mentioned that declining residential demand may also impact gas distribution networks, raising concerns about stranded assets and potential costs for end users.
The report highlights the critical role of natural gas in Australia’s energy transition and warns of the challenges ahead. Declining east coast supply, rising reliance on imports, and links to volatile international markets risk driving up prices. This price increase would likely flow through to energy prices, impacting the southern states in particular. With gas-powered generation needed to fill the gaps of solar and wind, action is required to secure supply and invest in new infrastructure. Will the necessary steps be taken in time?