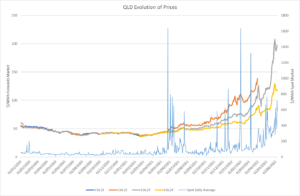
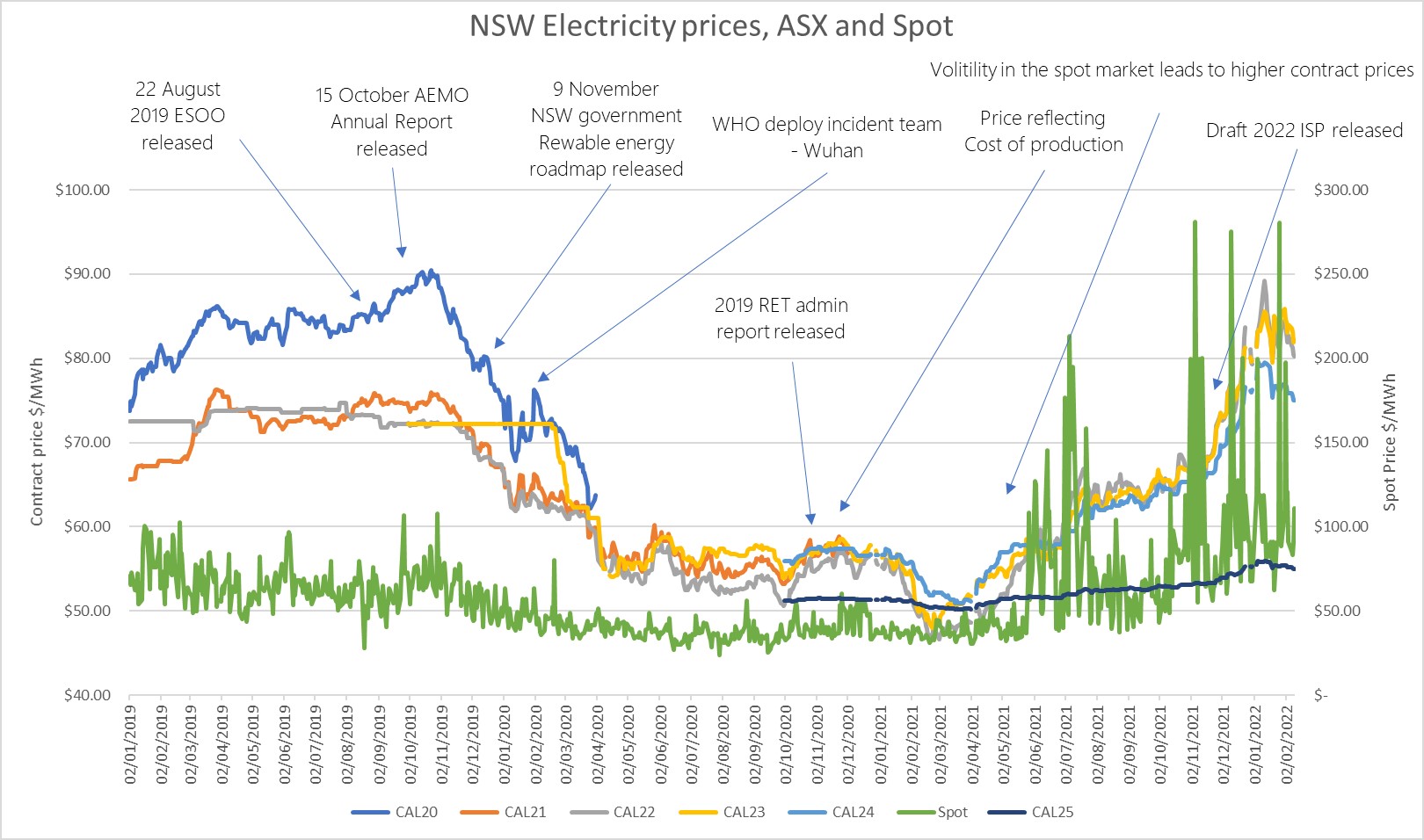
Whilst some were still tending hangovers from new year celebrations, January 2nd was the start of rallies in a Southwestern oil town of Zhanaozen in Kazakhstan and this unrest soon spread to most major towns and cities across the country.
To understand the country of 19 million and its enormous wealth you need to go back to the fall of the Soviet Union in 1991 when the country gained its “independence,” I am using the term independence lightly!!
As an oil rich nation (it is estimated it produces 1.6 million barrels of oil per day), a government, despite locationally placed between Russia and China, being one which is firmly in the Russian pocket and for nearly thirty years being run by one man, Nursultan Nazarbayev (a close ally of Vladimir Putin), you imagine significant wealth being distributed to the small population of this huge wealthy country (which is larger than Western Europe), but this is not the case.
Nazarbayev focused on economic reform over democracy. He erected statues of himself all over the country and created a new capital which although originally named Astana (literally translated as “Capital”) was re-named Nur-Sultan after himself until the end of his term when it reverted to Astana. He stood down in 2019, however, continued to hold a significant stronghold over the country as the head of Kazakhstan’s Security Council and “Father of the Nation”.
His successor was President Tokayev. He was a protégé of Nazarbayev and is also close to Putin, however, unlike his peers he doesn’t seem to have any business interest in or outside of Kazakhstan. There are no corruption scandals surrounding him, his diplomatic skills and manners are irrefutable and as a speaker of five languages and a successful diplomatic career, including serving in the USSR embassy in Beijing during the Tiananmen Square massacre in 1989, he is seen to be a quiet, interim holder of the position until it was assumed Nazarbayev’s daughter takes the reigns. However, he is now, for the first time, able to show his real intentions. This is due to Nazarbayev supposedly fleeing the country following this latest unrest.
The small oil town of Zhanaozen, which has a history of riots, with deadly clashes 10 years ago starting in the town, which led to legislation stating public protests are now illegal without government permits, once again on January 2nd took centre stage for the start of the latest situation.
What started as peaceful protests around the removal of the price cap on liquified petroleum gas (which many Kazakhs converted their vehicles to due to it being a cheaper alternative) was hijacked and has led to many asking if this really is the end of the Nazarbayev era?
The removal of the price cap doubled the price of the fuel overnight and is no doubt driven by the opportunity to re-coup greater value of the fuel abroad, especially in western Europe which is currently suffering from a lack of supply and record high prices.
But soon many others, mainly young, disillusioned Kazakhs who wanted to protest against the mass corruption within the country and the chasm of disparity in the country’s socio-economic situation, joined the protests. Although illegal these protests were peaceful and were mainly unorganised gatherings of unemployed countryside youths who wanted to express their feelings of social injustice.
This changed on January the fifth. At this point, thousands of armed mercenaries joined the protests in the city of Almaty. They seized the airport, police stations and administrative buildings and were protesting Mr Tokayev’s government and the former president Mr Nazarbayev.
To quell the violence and restore order to what was once seen to be one of the most stable states in central Asia, Mr Tokayev called in Russian led “peacekeepers” from the Collective Security Treaty Organisation (CSTO, made up of Russia, Belarus, Armenia, Kazakhs, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan forces) who had the right to fire without warning and although reports are varying the clashes led to 225 protesters and law enforcement personnel being killed.
Curfews were declared and mass gatherings were banned. Even China has declared they would help increase “law enforcement and security” to avoid the influence of the “foreign militants” and “terrorists”. President Tokayev stated that over “20,000 bandits” hijacked these protests with many being Islamic Militants, groups which although not named were said to have trained outside of the country.
By the time Ash Barty took to the final of the Adelaide open to face the Russian born Kazakh, Elena Rybankina, on Sunday 9th the fires were dampening and riots calming. The Kazakh government, after a short period of dissolution, now firmly back in place, are disclosing they have arrested around 12,000 people for participation in the protests however in a state where the cards are held so close to their chests the death toll and arrest numbers could be significantly higher.
But the reason so many eyes are centred on this oil-rich nation is that for the first time in thirty years the deep reforms necessary and old elitist viewpoints can be addressed. No one expects Mr Tokayev to become a man of the people and completely disassemble the economic and political power his close associates hold, no matter how many CEOs, who happen to be sons-in-law of Nazarbayev, are asked to leave their positions. But he does have the opportunity to step out of Nazarbayev’s huge shadow and become his own figure.
This is already starting with an unprecedented attack on Nazarbayev, saying his mentor had failed to share the country’s vast wealth with ordinary Kazakhs and announcing wide ranging reforms which are aimed at winning popular support amongst ordinary Kazakhs, including setting up a new fund for the public good to which oligarchs and wealthy businessman will be forced to contribute.
The injustice in the resource distribution outside of the oligarchy and corruption that follows is not part of Mr Tokayev’s makeup and this could be critical now, especially whilst those loyal to Nazarbayev are still holding many economic reigns in Kazakhstan.
Mr Tokayev, although now in a stronger position, is at a tipping point of shifting the country towards democracy or continuing down his predecessor’s path. Either way as a country rich in oil reserves and one crying out for structural reform, this is no doubt an opportunity and one many across the world are watching very closely.
Article was written by Kate Turner Senior Manager Markets, Analytics & Sustainability