Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC+), the intergovernmental organisation of 23 oil exporting nations mainly in the Middle East and Africa (with the original core 13 holding most power) is the body which is responsible for around 40% of the world’s oil production. In early October this group agreed to slash the output of crude oil by 2 million barrels a day. To put this in perspective Saudi Arabia produces on average 10 million barrels per day of the current, already reduced, 42 million barrels coming from the OPEC+ nations and this 2-million-barrel reduction translates to about 2% of the global oil supply. It is also worth noting in 2016 when OPEC became OPEC+ Russia joined the organisation and has held a strong voice ever since.
This reduction in production, shows a sign of deepening rifts between the Middle East and the US, and the cynic in me says may be more than slightly linked to the upcoming US mid-term elections where the democrats are already looking weaker than their GOP counterparts – not that those countries have ever influenced an American election in the past *Cough Trump Cough*. But regardless of motives these new production limits will come into place in November and the impending reduction in production has repercussions which flowed through the broader Australian and global energy markets including oil, coal and gas.
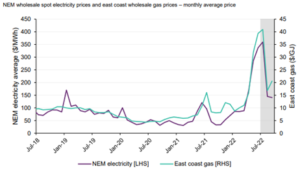
Australian electricity prices are strongly correlated with the international crude oil price, particularly in QLD and NSW, the impact of Brent crude futures hitting a high of $US93.39 on Monday caused a rally on the Australian electricity market, with the Q123 QLD price rising 20%, as the effect of this increase translated to the domestic electricity market. Brent Crude being the international oil benchmark price.
However, OPEC+ are not the only drivers of the oil price, especially WTI and Brent prices. The US dollar, on the back of a fear of a global recession has been strengthening which has dampened the demand for their oil on the international stage. (Consider the FX implications of a strong dollar, if you are buying from Europe the same amount of crude oil now costs more as the number of Euros to achieve the same dollar amount has increased). So, a reduction in demand of America Oil due to FX and reduction in export from OPEC+ can only move the needle up in price regardless of source.
We also cannot ignore the ongoing COVID implications in Asia, especially China. Their glut of demand has not returned to anywhere near the pre-pandemic levels and as such that demand is not translating into a price war to ensure delivery of the commodity. Conversely to above this is actually holding prices lower and reducing the impact of the OPEC+ reduction.
But there is no ignoring the elephant in the room, the impact of Russia’s invasion of the Ukraine, which has led to global increases in commodity costs, has also acted as a buffer to the oil price despite the recession fears. As many countries imposed their own moral code and refused to buy Russian oil, other sources could benefit from the increase in demand. By the end of September this year Russian oil was trading at $20/barrel cheaper than its Brent counterpart. Some less scrupulous countries such as India and China, sought to benefit from this price differential and ignored the sanctions coming from the West and are now taking at least half of Russia’s oil exports. Further, Russia has now overtaken Saudi Arabia to be the biggest exporter of oil into China. Therefore, could the cut in reduction be as simple as the rest of OPEC+ looking to balance the loss in demand from the East by passing inflated prices to the West?
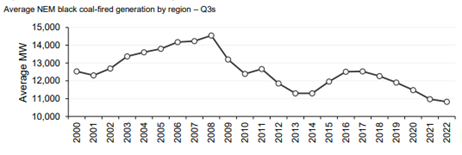
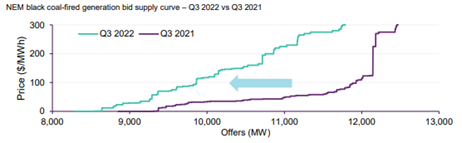
But back to Australia, we are obviously a commodity rich nation, however with our internal thirst for electricity and therefore generation linked heavily to the export price of that commodity, we are subject to these international fluctuations also. As the price of the oil increases, the global demand from that commodity shifts to other sources. Our gas and coal price domestically are therefore linked heavily to the price that exporters can achieve if they send our home-grown coal and gas abroad. So as the demand shifts from oil, to gas or coal so does the price. Hence the correlation described above with Brent rising and that coming into our domestic market.
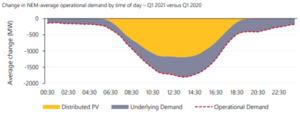
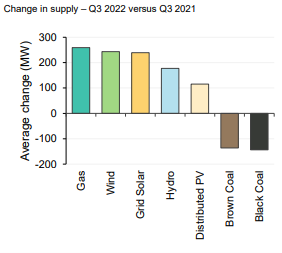
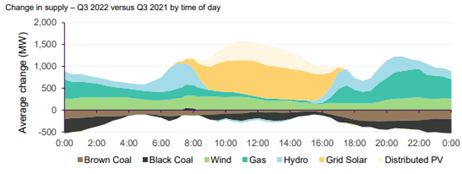
Then for fun lets add in our own pressures, we are expecting another La Nina this year, last year’s summer La Nina brought low solar output coupled with flooding, wet coal stockpiles and just-in-time delivery delays due to the tracks being flooded and trains not able to deliver.
We also have an economy which is having increasing inflationary pressures. These inflation increases will flow onto the interest rates (including the interbank rates) and therefore commodity prices. How? Well, a retail return is based on 2 main drivers, network and wholesale costs, the latter we have covered above. But in isolation network costs will also increase, due to the inflation increasing the nominal value of the asset and therefore the increasing value of the debt as the interest rates increase also.
Further any investment required to transition our market to greener fuels will also be increased, as the levelized cost of electricity for these new assets is also increased due to cost of capital and higher interest rates feeding through. As such the ‘Energy transition’ will now cost more.
There is also a regulatory driver, with an impending price cap increase being fast tracked, this will allow system stability to flow through, as gas won’t withdraw at the $300/MWh cap as this looks likely to be increased to $500/MWh. Therefore, does that become the new ceiling of our market?
There is an old idiom that when China sneezes Asia catches a cold, I unfortunately think this now needs to be broadened to when any imbalance occurs the ripples will be felt globally.
The balance is so tight that without some easing of any fundamentals the shocks will continue. AEMO are acknowledging this, but despite acknowledging the issues they are desperately clinging to the hope a capacity market will be the silver bullet to system stability, backed by large synchronous generators, not that they have any benefit from that mechanism. However, I cannot agree, point in fact I point you to the black outs in the UK on August 9th 2019, a market which has had a capacity mechanism for many years yet in a moment of system instability these ‘capacity assets’ could do nothing and they experienced a blackout for 45 minutes and over 1 million people were affected.
What this means for us is without regulation around bidding behaviour based on cost of generation from hedges not advantageous forward prices, we are looking at another summer with uncertainty and volatility based on international fundamentals pulling the Australian market along for the ride.